Neurological Disorders
A neurological disorder ais any condition that is caused by a dysfunction in part of the brain or nervous system. Patients experience physical and/or psychological symptoms.
All neurologic disorders involve the brain, spinal column or nerves. Symptoms depend on where damage occurs. Areas that control movement, communication, vision, hearing or thinking can be affected.
The development of the brain starts in pregnancy and goes through infancy, childhood and adolescence. Most brain cells are formed before birth but the trillions of connections between these nerve cells (neurons) are only developed on infancy.
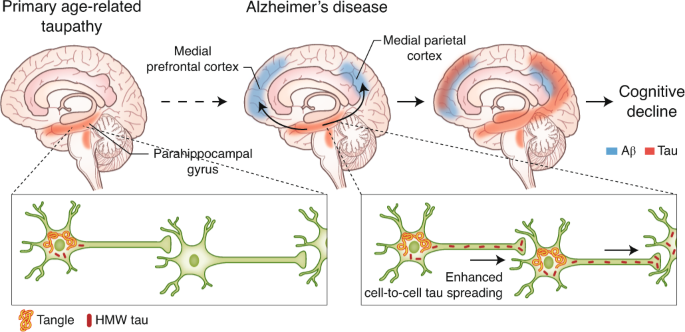
Alzheimer's
The brain normally shrinks to some degree in healthy aging but does not lose neurons in large numbers. In Alzheimer’s disease, however, damage is widespread, as many neurons stop functioning, lose connections with other neurons, and die.
Alzheimer’s disrupts processes vital to neurons and their networks, including communication, metabolism, and repair.
Alzheimer's and Amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques
Large deposits of amyloid beta are believed to cause neurological destruction that results in Alzheimer’s.
Amyloid beta formed in the brain’s axons and nerve endings causes the worst damage in Alzheimer’s by impairing communication between nerve cells, or neurons, in the brain.
Researchers around the world have worked intensely to find ways to block the formation of amyloid beta by preventing cleavage by beta secretase and gamma secretase. However, these approaches have been hampered by safety issues.